 PDF(1755 KB)
PDF(1755 KB)


The Chemical Characteristics and Their Influencing Factors of Moss Layer Penetration Rain in Northern Da Xing′an Mountains
Xintao WANG, Xiaoying FAN, Jinhao ZHANG, Yushan CAI, Liangliang DUAN
Forest Engineering ›› 2025, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2) : 266-276.
 PDF(1755 KB)
PDF(1755 KB)
 PDF(1755 KB)
PDF(1755 KB)
The Chemical Characteristics and Their Influencing Factors of Moss Layer Penetration Rain in Northern Da Xing′an Mountains
Moss plays an important role in forest water conservation, nutrient fixation and water quality regulation. In order to reveal the influence of mosses on the water chemical characteristics of forest rainfall redistribution, this study selected Sphagnum and Pleurozium schreberi as research objects, and observed and studied the moss layer penetration rain and water chemical characteristics of the two mosses in the growing season from June to September of 2023. The results showed as follows: the maximum water holding capacity, maximum water holding rate and thickness of Sphagnum were significantly (P<0.01) higher than those of Pleurozium schreberi. There were differences in ion concentration between the two species of moss penetration rain. K+ showedthe most significant leaching effect of Sphagnum and F- showedthe most significant retention effect. The K+ concentration increased by 241% after passing through the Sphagnum layer compared with the canopy penetration rain, while the F- concentration decreased by 51.6%. The total metal ion concentration increased by 71.7% after passing through the Sphagnum layer, while the total concentration of nonmetallic ions decreased by 19.9%.
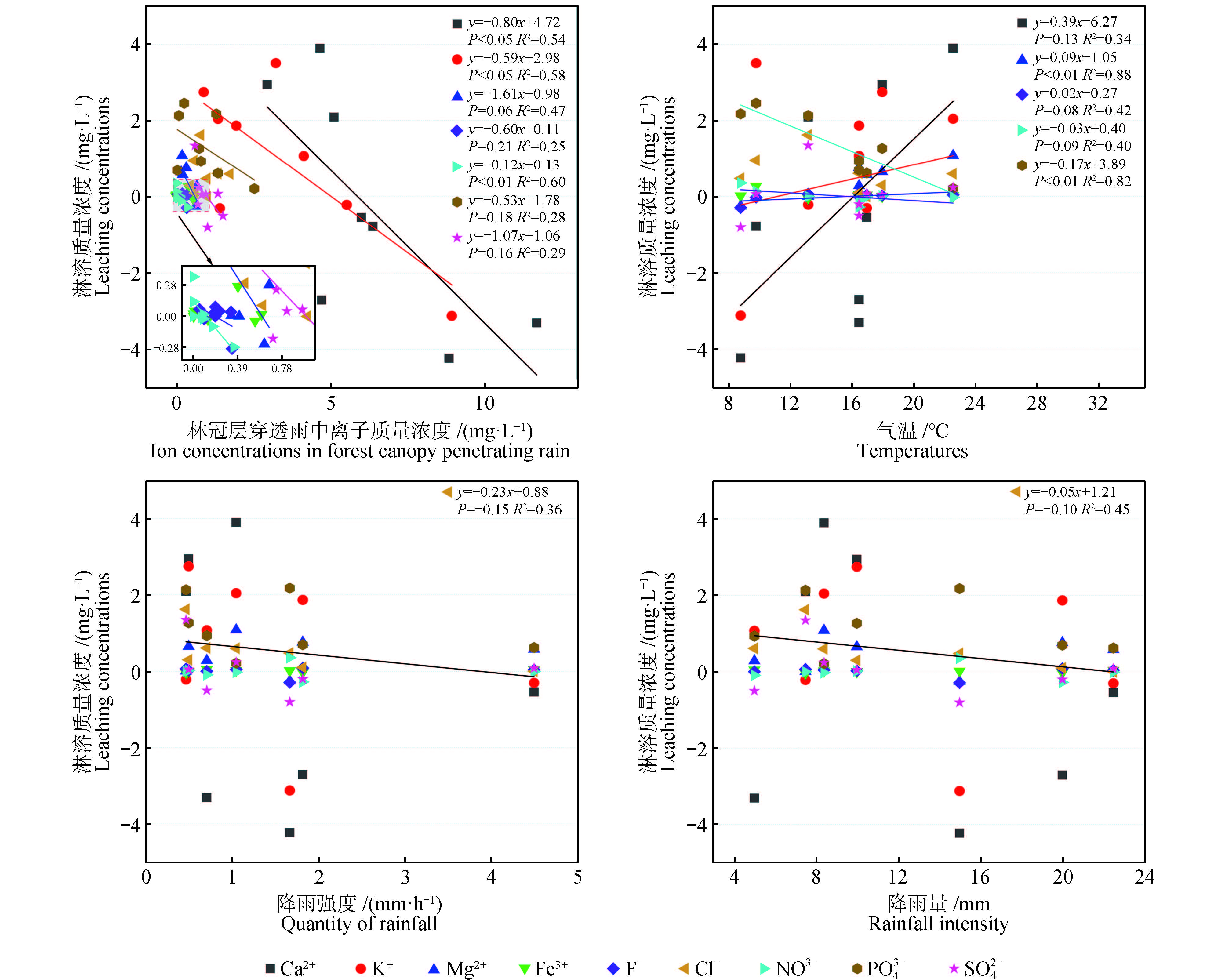
Northern Da Xing'anling Mountains / moss layer penetration rain / water chemistry / anion / cation {{custom_keyword}} /
| 1 | SLATE M L, SULLIVAN B W, CALLAWAY R M.Desiccation and rehydration of mosses greatly increases resource fluxes that alter soil carbon and nitrogen cycling[J].Journal of Ecology,2019,107(4):1767-1778. |
| 2 | 张文静,程建峰,刘婕,等.植物铁素(Fe)营养的生理研究进展[J].中国农学通报,2021,37(36):103-110. |
| ZHANG W J, CHENG J F, LIU J,et al.Nutrition physiology of iron (Fe) in plants: research progress[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2021,37(36):103-110. | |
| 3 | 郝占庆,叶吉,姜萍,等.长白山暗针叶林苔藓植物在养分循环中的作用[J].应用生态学报,2005,16(12):2263-2266. |
| HAO Z Q, YE J, JIANG P,et al.Roles of bryophyte in nutrient cycling in dark coniferous forest of Changbai Mountains[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2005,16(12):2263-2266. | |
| 4 | DAI S, KITUDOM N, MIAO X,et al.Assessing precipitation redistribution and hydro-chemical dynamics in a high-elevation evergreen broad-leaved forest[J].Forests,2023,14(11):2239. |
| 5 | 冯亚琦,郭娜,蔡体久,等.蒙古栎林对大气降雨的再分配规律[J].森林工程,2017,33(5):24-28,34. |
| FENG Y Q, GUO N, CAI T J,et al.Rainfall redistribution of mongolian oak plantation in Harbin[J].Forest Engineering,2017,33(5):24-28,34. | |
| 6 | 孙向阳,王根绪.贡嘎山森林生态系统降水分配的水化学特征研究[J].水土保持研究,2009,16(6):120-124. |
| SUN X Y, WANG G X.The hydro-chemical characteristics study of forest ecosystem precipitation distribution in Gongga Mountain[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2009,16(6):120-124. | |
| 7 | 常竣泊,马哲宇,丁忠杰,等.植物种子铁储存、运输和再利用分子机制的研究进展[J].浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2021,47(4):473-480. |
| CHANG J B, MA Z Y, DING Z J,et al.Research progresses on molecular mechanisms of storage,transportation and reutilization of plant seed iron[J].Journal of Zhejiang University(Agriculture and Life Sciences),2021,47(4):473-480. | |
| 8 | 高冲,杨肖娥,向律成,等.pH和温度对薏苡植物床去除富营养化水中氮磷的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2008,27(4):1495-1500. |
| GAO C, YANG X E, XIANG L C,et al.The effects of pH and temperature on removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from eutrophicated water by Coix lachrymajobi L.[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2008,27(4):1495-1500. | |
| 9 | 邹志谨,陈步峰.广州市帽峰山两种主要林型的暴雨水文特征[J].生态环境学报,2017,26(5):770-777. |
| ZOU Z J, CHEN B F.Hydrological features of rainstorms in two forest types in Maofeng mountain of Guangzhou[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2017,26(5):770-777. | |
| 10 | 盛后财,姚月锋,蔡体久,等.物候变化对落叶松人工林降雨分配过程中钾和钠离子迁移的影响[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2021,45(6):143-150. |
| SHENG H C, YAO Y F, CAI T J,et al.Effects of phenoseason on transfer of potassium and sodium ions in the process of rainfall redistribution in larch (Larix gmelinii) plantations[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Sciences Edition),2021,45(6):143-150. | |
| 11 | WILLIAMSON T N, SENA K L, SHODA M E,et al.Four decades of regional wet deposition,local bulk deposition,and stream-water chemistry show the influence of nearby land use on forested streams in Central Appalachia[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2023,332:117392. |
| 12 | 廖佩琳,高全洲,杨茜茜,等.酸沉降背景下鼎湖山林区径流的水化学组成特征[J].生态学报,2022,42(6):2368-2381. |
| LIAO P L, GAO Q Z, YANG Q Q,et al.Hydrochemical compositions characteristics of runoff in Dinghushan forest region under the background of acid deposition[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2022,42(6):2368-2381. | |
| 13 | 萨如拉.大兴安岭南部山地苔藓植物区系及多样性研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2015. |
| SA R L.A study on the diversity within the bryoflora of southern Greater Khingan Mountains China[D].Hohhot:Inner Mongolia University,2015. | |
| 14 | 盛后财.大兴安岭北部兴安落叶松林生态水文特征研究[D].哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2021. |
| SHENG H C.Ecohydrological characteristics of Larix gmelinii forest in the north of Daxing'an Mountains[D].Harbin:Northeast Forestry University,2021. | |
| 15 | 涂娜,严友进,戴全厚,等.喀斯特石漠化区典型生境下石生苔藓的固土持水作用[J].生态学报,2021,41(15):6203-6214. |
| TU N, YAN Y J, DAI Q H,et al.Soil fixation and water retention of rocky moss under typical habitat in a karst rocky desertification area[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(15):6203-6214. | |
| 16 | 李岳泰,满秀玲,喻武,等.不同地形樟子松天然林土壤呼吸特征及其影响因素[J].森林工程,2020,36(1):1-9,24. |
| LI Y T, MAN X L, YU W,et al.Soil respiration characteristics and influencing factors of Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica natural forest under different terrain[J].Forest Engineering,2020,36(1):1-9,24. | |
| 17 | 李军峰,王智慧,张朝晖.喀斯特石漠化山区苔藓多样性及水土保持研究[J].环境科学研究,2013,26(7):759-764. |
| LI J F, WANG Z H, ZHANG Z H.Bryophyte diversity and the effect of soil formation along with water conservation in karst rocky desertification region[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2013,26(7):759-764. | |
| 18 | 王芝慧,白义,李飞,等.川西亚高山森林木质残体及其附生苔藓持水特性[J].生态学报,2021,41(16):6552-6565. |
| WANG Z H, BAI Y, LI F,et al.Water-holding characteristics of woody debris and epiphytic moss in the subalpine forest of western Sichuan[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(16):6552-6565. | |
| 19 | AUDE E, EJRN?S R.Bryophyte colonisation in experimental microcosms:The role of nutrients,defoliation and vascular vegetation[J].Oikos,2005,109(2):323-330. |
| 20 | 吴玉环,高谦,程国栋,等.苔藓植物对全球变化的响应及其生物指示意义[J].应用生态学报,2002,13(7):895-900. |
| WU Y H, GAO Q, CHENG G D,et al.Response of bryophytes to global change and its bioindicatortation[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2002,13(7):895-900. | |
| 21 | 刘一霖,温娅檬,李巧玉,等.川西高山峡谷区6种森林枯落物的持水与失水特性[J].水土保持学报,2019,33(5):151-156,162. |
| LIU Y L, WEN Y M, LI Q Y,et al.Water holding and water-loss characteristics of six types of forest litter in the alpine gorge region of western Sichuan[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,33(5):151-156,162. | |
| 22 | 刘润,申家琛,张朝晖.4种苔藓植物在喀斯特石漠化地区的生态修复意义[J].水土保持学报,2018,32(6):141-148. |
| LIU R, SHEN J C, ZHANG Z H.Study on the significance of ecological restoration of four bryophytes in karst rocky desertification area[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,32(6):141-148. | |
| 23 | 陈国鹏,曹秀文,王会儒,等.白龙江干旱河谷岩生植物持水性能[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(1):102-105. |
| CHEN G P, CAO X W, WANG H R,et al.Water holding capacity of rock plant species in dry valley at the Bailongjiang river of Gansu Province[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2014,28(1):102-105. | |
| 24 | 王照.参与刺梨钙吸收相关基因的鉴选与表达特征[D].贵阳:贵州大学,2022. |
| WANG Z.Identification and expression characteristics of genes involved in calcium absorption in Rosa roxburghii Tratt[D].Guiyang:Guizhou University,2022. | |
| 25 | 郎燕,蔡体久,柴汝杉,等.不同类型原始红松林对降雨水化学特征的影响[J].水土保持学报,2012,26(2):184-191. |
| LANG Y, CAI T J, CHAI R S,et al.Effects of different types of original Pinus korainensis forest on precipitation hydro chemical characteristics[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2012,26(2):184-191. | |
| 26 | 车宗玺,刘贤德,敬文茂,等.祁连山林区苔藓垂直分布特征与水文功能分析[J].水土保持学报,2006,20(6):71-74. |
| CHE Z X, LIU X D, JING W M,et al.Vertical distribution characteristics and hydrological function analysis of bryophytes in Qilian Mountains forest areas[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2006,20(6):71-74. | |
| 27 | 刘茜,满秀玲,田野宏.白桦次生林降雨水化学及养分输入特征[J].北京林业大学学报,2015,37(8):83-89. |
| LIU X, MAN X L, TIAN Y H.Hydro-chemical and nutrient importing characteristics of precipitation in secondary Betula platyphylla forests in northern Great Xing′an Mountains,northeastern China[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2015,37(8):83-89. | |
| 28 | 李伟,张胜利,孟庆旭,等.秦岭华山松林生态系统对大气降雨水化学特性的影响[J].西北林学院学报,2016,31(5):15-22. |
| LI W, ZHANG S L, MENG Q X,et al.Effects of Pinus armandii forest ecosytem on the chemical features of atmospheric rainfall water in Qinling mounstains[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2016,31(5):15-22. | |
| 29 | 卢晓强,杨万霞,丁访军,等.茂兰喀斯特地区森林降水分配的水化学特征[J].生态学杂志,2015,34(8):2115-2122. |
| LU X Q, YANG W X, DING F J,et al.Reallocation and chemical characteristics of precipitation in a Maolan karst forest[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2015,34(8):2115-2122. | |
| 30 | 张伟,杨新兵,李军.冀北山地华北落叶松林生态系统水化学特征[J].水土保持学报,2011,25(4):217-220. |
| ZHANG W, YANG X B, LI J.Precipitation hydrochemical characteristic of north deciduous pine of north mountain of Hebei Province[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2011,25(4):217-220. | |
| 31 | 赵维彬,王松,刘玲玲,等.生物炭改良盐碱地效果及其对植物生长的影响研究进展[J].土壤通报,2024,55(2):551-561. |
| ZHAO W B, WANG S, LIU L L,et al.Effect of biochar amendment on saline-alkaline soil amelioration and plant growth:A literature review[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2024,55(2):551-561. | |
| 32 | 雷丽群,韦菊玲,农友,等.森林生态系统水化学效应研究综述[J].林业调查规划,2016,41(6):24-29. |
| LEI L Q, WEI J L, NONG Y,et al.Review on the effects of forest ecosystem on water chemistry[J].Forest Inventory and Planning,2016,41(6):24-29. | |
| 33 | SNYDER K A, WILLIAMS D G.Water sources used by riparian trees varies among stream types on the San Pedro River,Arizona[J].Agricultural & Forest Meteorology,2000,105(1/3):227-240. |
| 34 | 杨莉莉.氯对猕猴桃生长发育和产量品质的影响及其作用机理[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2021. |
| YANG L L.Effect of chlorine on growth,yield and fruit quality of kiwifruit and its mechanism[D].Yangling:Northwest A & F University,2021. | |
| 35 | 王东旭,贾志红,周文辉,等.氯离子在不同质地植烟土壤中的迁移及烟株中的积累[J].中国烟草学报,2022,28(1):68-77. |
| WANG D X, JIA Z H, ZHOU W H,et al.Migration of chloride ion in tobacco-planting soil with different textures its accumulation in tobacco plants[J].Acta Tabacaria Sinica,2022,28(1):68-77. | |
| 36 | WEGE S, GILLIHAM M, HENDERSON S W.Chloride:not simply a ‘cheap osmoticum’,but a beneficial plant macronutrient[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2017,68(12):3057-3069. |
| 37 | COLMENERO-FLORES J M, FRANCO-NAVARRO J D, CUBERO-FONT P,et al.Chloride as a beneficial macronutrient in higher plants:New roles and regulation[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(19):4686. |
| 38 | XU G H, MAGEN H, TARCHITZKY J,et al.Advances in chloride nutrition of plants[J].Advances in Agronomy,1999,68:97-110. |
| 39 | SHENG H, CAI T.Influence of rainfall on canopy interception in mixed broad-leaved—korean pine forest in Xiaoxing'an Mountains,northeastern China[J].Forests,2019,10(3):248. |
| 40 | BRASELL H M, MATTAY J P.Colonization by bryophytes of burned eucalyptus forest in Tasmania,Australia:Changes in biomass and element content[J].Bryologist,1984,87(4):302-307. |
| 41 | 方运霆,莫江明, Gundersen Per,等.森林土壤氮素转换及其对氮沉降的响应[J].生态学报,2004,24(7):1523-1531. |
| FANG Y T, MO J M,PER G,et al.Nitrogen transformations in forest soils and its responses to atmospheric nitrogen deposition:A review[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2004,24(7):1523-1531. | |
| 42 | ELLSWORTH P Z, WILLIAMS D G.Hydrogen isotope fractionation during water uptake by woody xerophytes[J].Plant and Soil,2007,291(1-2):93-107. |
| 43 | BARROW N J, LAMBERS H.Phosphate-solubilising microorganisms mainly increase plant phosphate uptake by effects of pH on root physiology[J].Plant and Soil,2022,476(1):397-402. |
| 44 | DAI S, KITUDOM N, MIAO X,et al.Assessing precipitation redistribution and hydro-chemical dynamics in a high-elevation evergreen broad-leaved forest[J].Forests 2023,14(11),2239. |
| 45 | 邵俊雯,王婉瑕,李瑞莉,等.植物硫酸盐转运体研究进展[J].浙江农业科学,2023,64(6):1417-1425. |
| SHAO J W, WANG W X, LI R L,et al.Research progress of sulfate transporters in plants[J].Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2023,64(6):1417-1425. | |
| 46 | 宋彬,王得祥,张义,等.延安15种园林树种叶片硫含量特征分析[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2014,42(5):91-96. |
| SONG B, WANG D X, ZHANG Y,et al.Sulfur contents in foliage of 15 ornamental trees in Yan'an[J].Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Science Edition),2014,42(5):91-96. | |
| 47 | BORRELLY G P M, HARRISON M D, ROBINSON A K,et al.Surplus zinc is handled by Zym1 metallothionein and Zhf endoplasmic reticulum transporter in Schizosaccharomyces pombe[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2002,277(33):30394-30400. |
| 48 | WHITE P J, BROADLEY M R.Calcium in plants[J].Annals of Botany,2003,92(4):487-511. |
| 49 | 苏文,刘敬,王冰,等.植物高亲和钾离子转运蛋白HAK功能研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2020,36(8):144-152. |
| SU W, LIU J, WANG B,et al.Research progress on the HAK function of plant high affinity potassium ion transporter[J].Biotechnology Bulletin,2020,36(8):144-152. | |
| 50 | 刘茂炎.钾离子在水稻抗拟禾本科根结线虫中的功能分析[D].长沙:湖南农业大学,2021. |
| LIU M Y.The function analysis of potassium in rice resistance to meloidogyne graminicola[D].Changsha:Hunan Agricultural University,2021. | |
| 51 | TANG R J, LUAN S.Regulation of calcium and magnesium homeostasis in plants:from transporters to signaling network[J].Current Opinion in Plant Biology,2017,39:97-105. |
| 52 | 王蕾,哈斯,刘连友,等.北京市春季天气状况对针叶树叶面颗粒物附着密度的影响[J].生态学杂志,2006,25(8):998-1002. |
| WANG L,HA S, LIU L Y,et al.Effects of weather condition in spring on particulates density on conifers leaves in Beijing[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2006,25(8):998-1002. | |
| 53 | PRZYBYSZ A, S?B? A, HANSLIN H M,et al.Accumulation of particulate matter and trace elements on vegetation as affected by pollution level,rainfall and the passage of time[J].Science of the Total Environment,2014,481:360-369. |
| 54 | 王会霞,石辉,王彦辉.典型天气下植物叶面滞尘动态变化[J].生态学报,2015,35(6):1696-1705. |
| WANG H X, SHI H, WANG Y H.Dynamics of the captured quantity of particulate matter by plant leaves under typical weather conditions[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2015,35(6):1696-1705. | |
| 55 | 郭若妍,王会霞,石辉.模拟降雨对常绿植物叶表面滞留颗粒物的影响[J].生态学杂志,2019,38(7):1991-1999. |
| GUO R Y, WANG H X, SHI H.Effects of simulated rainfall on leaf particulate matter of different size fractions of evergreen plants[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2019,38(7):1991-1999. |
 PDF(1755 KB)
PDF(1755 KB)
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |